Real-time 3D Target Inference via Biomechanical Simulation
|
1
|
2

|
ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2024)
**Honorable Mention**
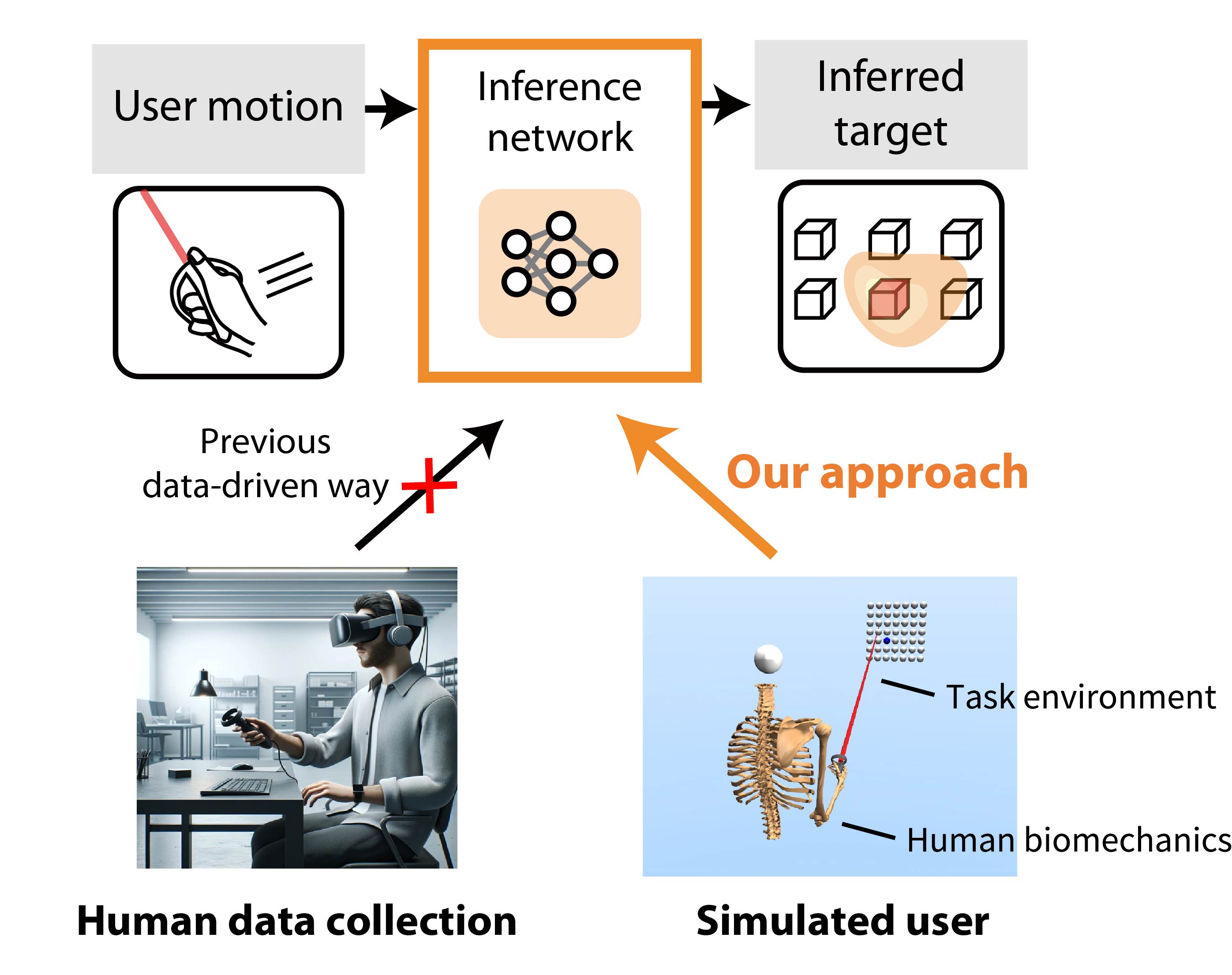
Can we generate realistic user data without involving humans?
|
•
Data-driven methods enable the inference of user intentions.
• However, the data collection process is expensive. • For new interactions with newly developed devices, training the model with a new dataset will be required. • Simulated users could significantly reduce the costs associated with traditional data collection. • We study simulated users to enhance actual users' selections in VR. |
|
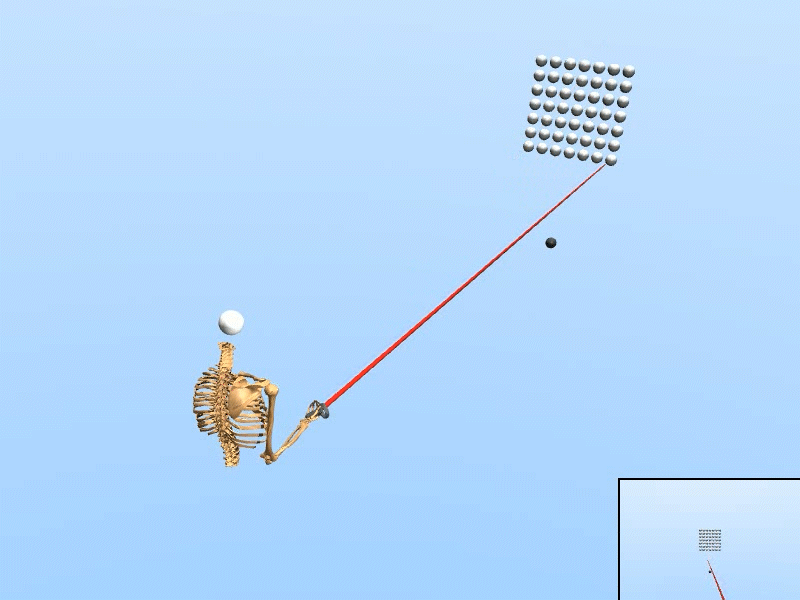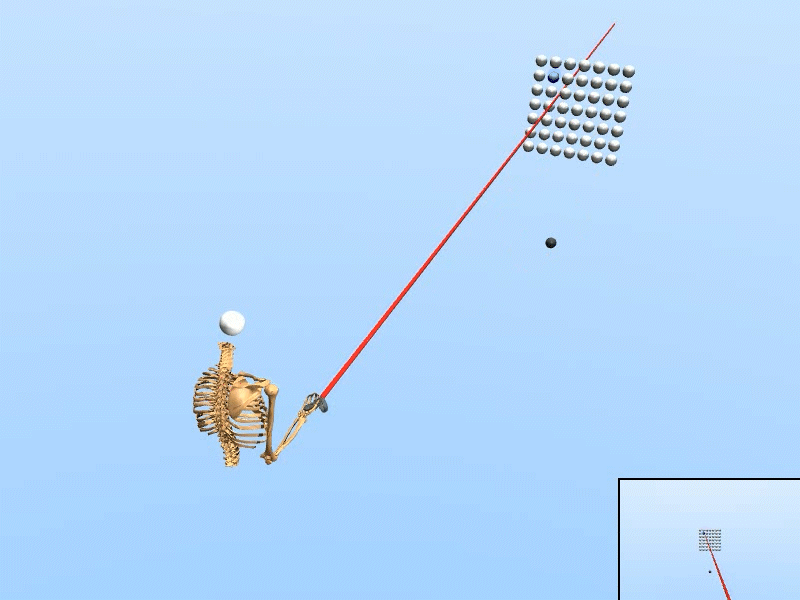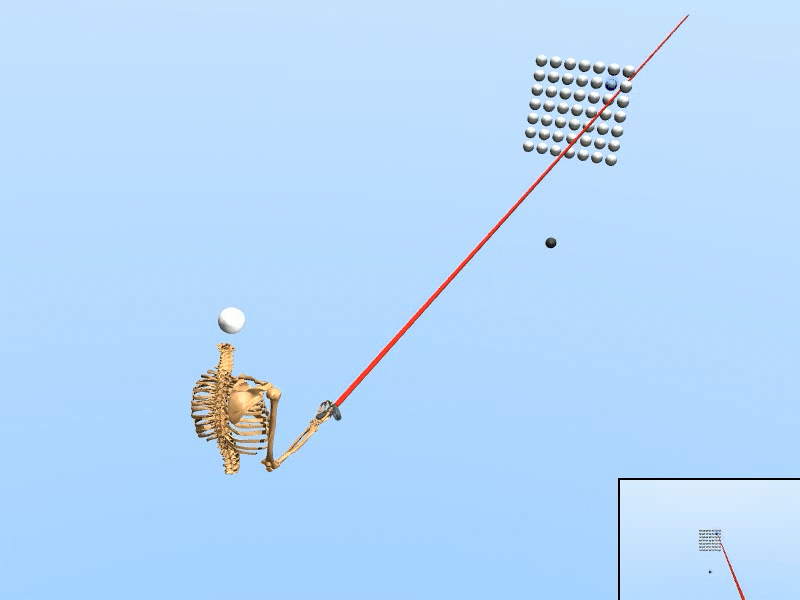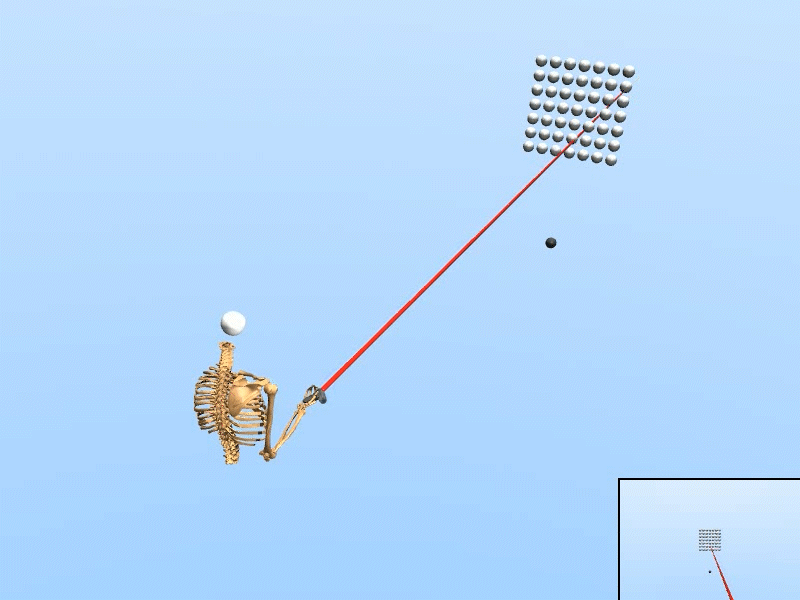
Simulated user with human-like perceptual and motor skills
|
Trained on Dense target grid
|
Trained on Wide target grid
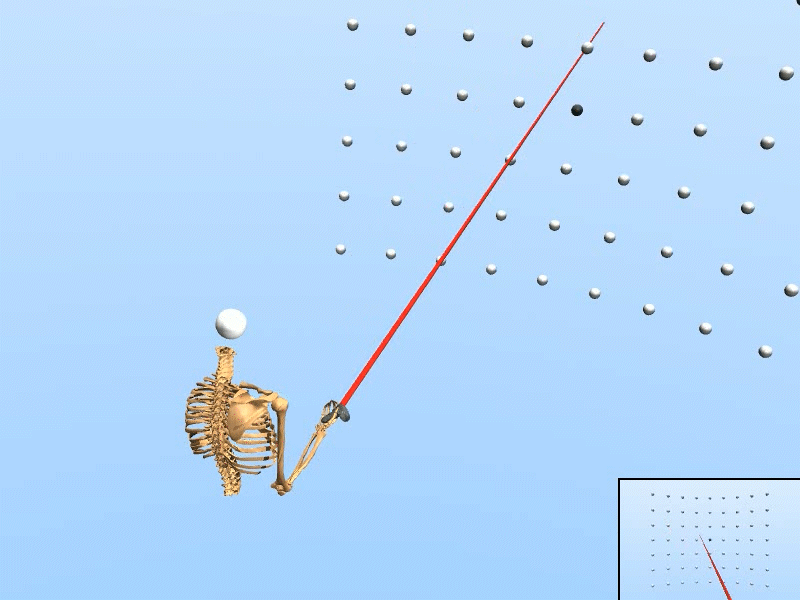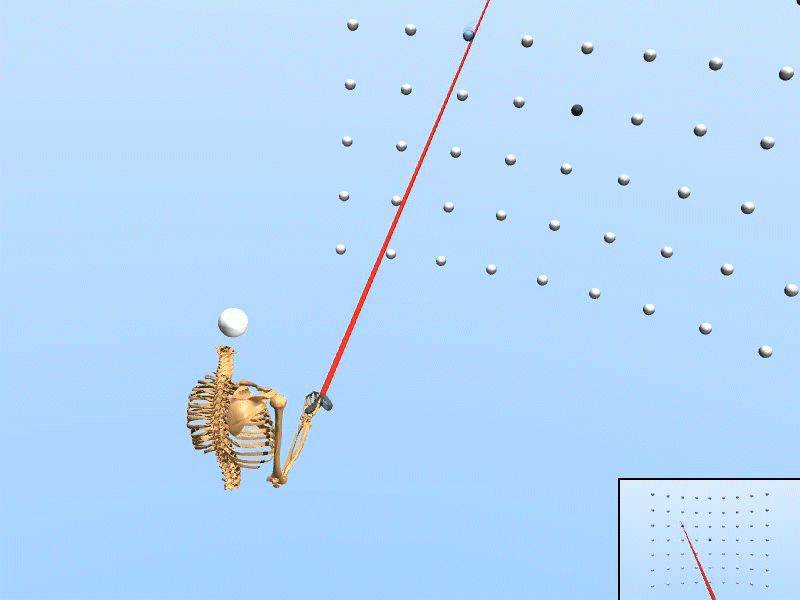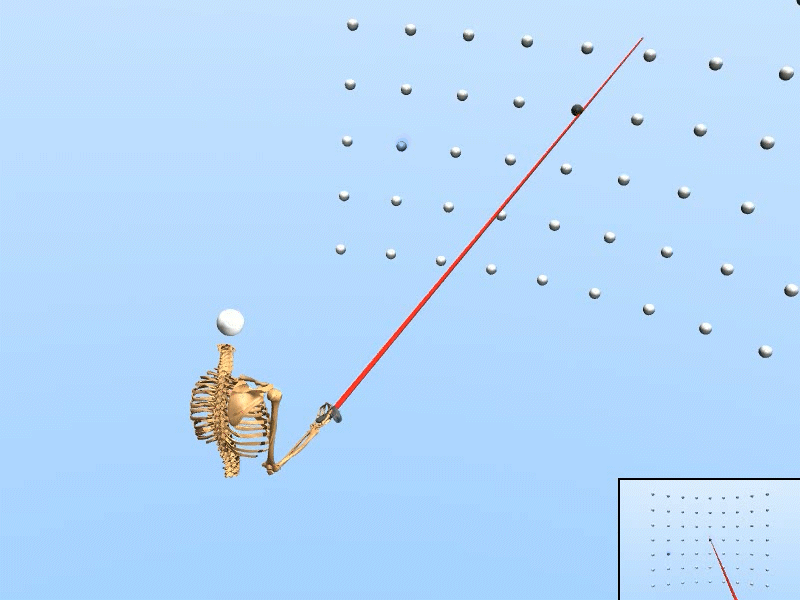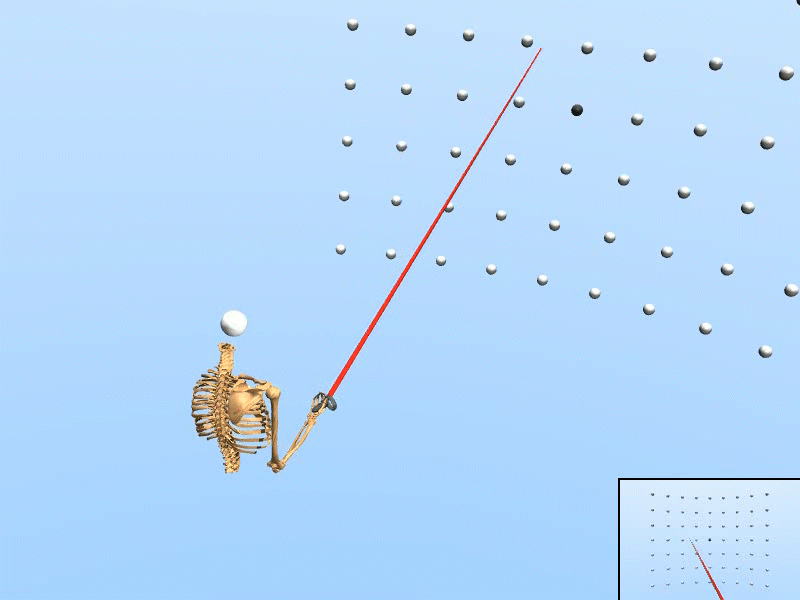
|
|
•
We created a rational agent with human-like perception and motor abilities, trained via reinforcement learning.
• The simulation adapts to various target configurations and user features. • Our simulated user replicated the task speed, accuracy, and motor variability of human users (N=20). • Using only simulated data, our inference accuracy equaled that achieved with data from seven human users. • The trained inference model enhanced selection speed and accuracy for human users in VR. |
Abstract
Selecting a target in a 3D environment is often challenging, especially with small/distant targets or when sensor noise is high. To facilitate selection, target-inference methods must be accurate, fast, and account for noise and motor variability. However, traditional data-free approaches fall short in accuracy since they ignore variability. While data-driven solutions achieve higher accuracy, they rely on extensive human datasets so prove costly, time-consuming, and transfer poorly. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that leverages biomechanical simulation to produce synthetic motion data, capturing a variety of movement-related factors, such as limb configurations and motor noise. Then, an inference model is trained with only the simulated data. Our simulation-based approach improves transfer and lowers cost; variety-rich data can be produced in large quantities for different scenarios. We empirically demonstrate that our method matches the accuracy of human-data-driven approaches using data from seven users. When deployed, the method accurately infers intended targets in challenging 3D pointing conditions within 5–10 milliseconds, reducing users' target-selection error by 71% and completion time by 35%.Citation
@inproceedings{moon2024real,
title={Real-time 3D Target Inference via Biomechanical Simulation},
author={Moon, Hee-Seung and Liao, Yi-Chi and Li, Chenyu and Lee, Byungjoo and Oulasvirta, Antti},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems},
year={2024},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
url = {https://hsmoon121.github.io/projects/chi24-target-inference},
doi = {10.1145/3613904.3642131},
location = {Honolulu, Hi, USA},
series = {CHI '24}
}